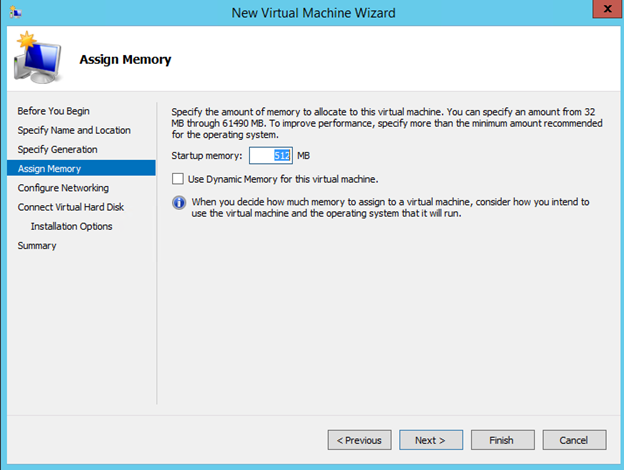
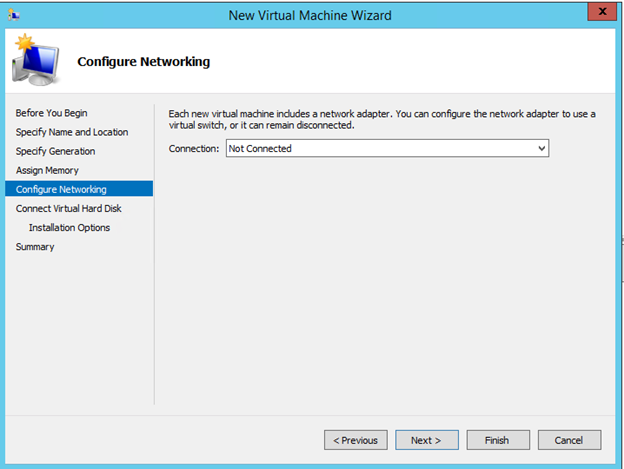
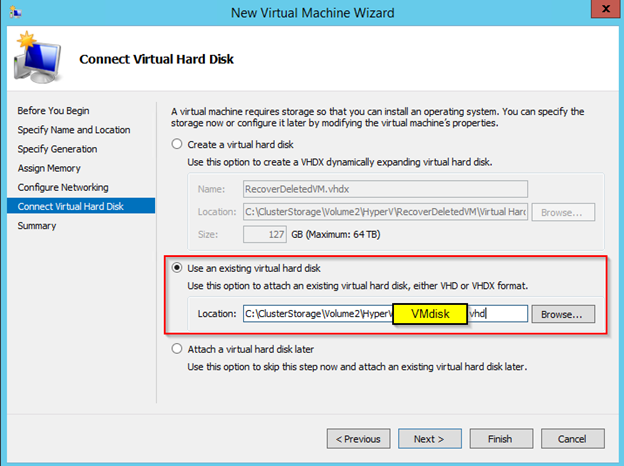
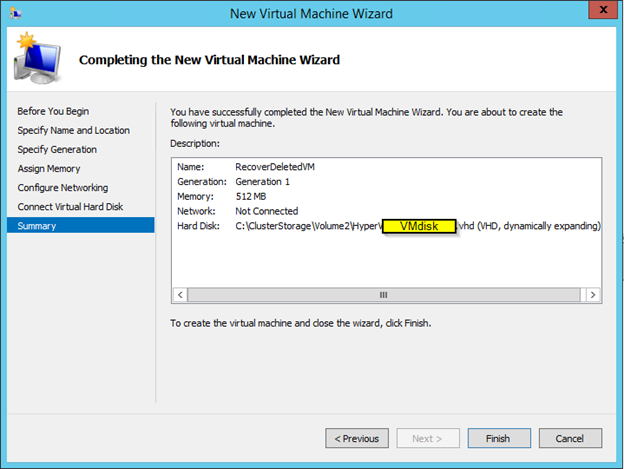
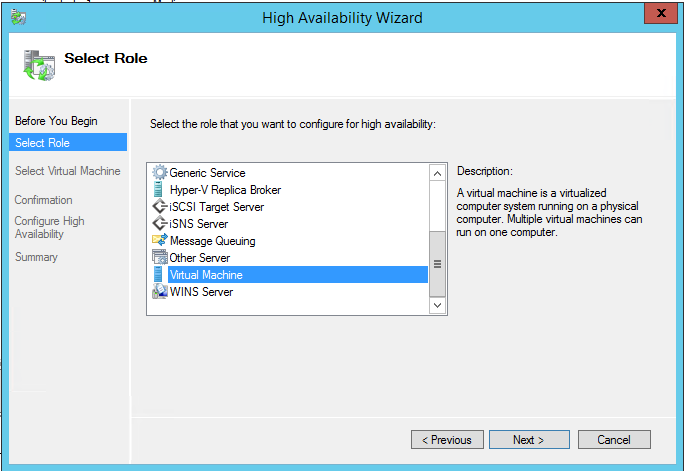
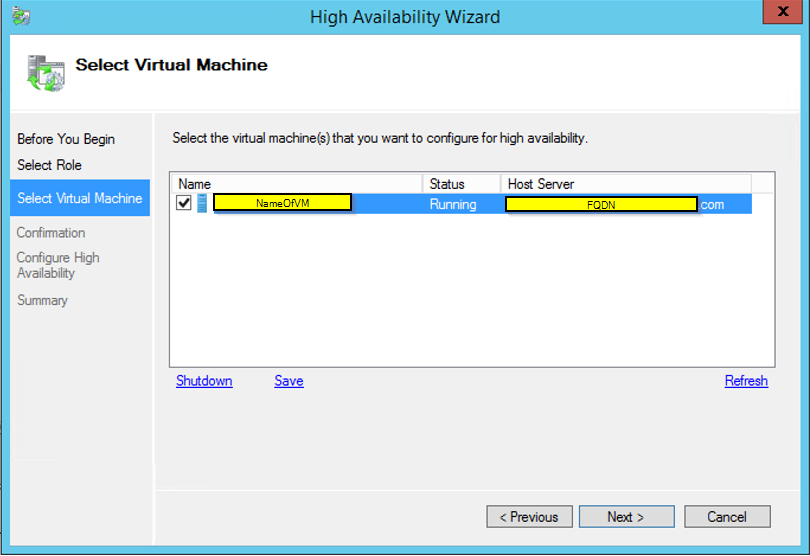
Hyper-V cluster is a very common business network uses, which allows system admin to do system updates, without having any downtime. There are times when VM (Virtual Machine) are created for a test or just got upgraded and left to be deleted later on. Cleaning up old VM will free up the storage space. In this post I will have steps on deleting VM from Hyper-V cluster, before deleting, check the location of the VM because deleting from the Cluster server, will not free up the storage, you will need to delete it manually. You can see the location of the VM by going to settings of the VM and select the Disk, it will display full path where your VM disk is stored.
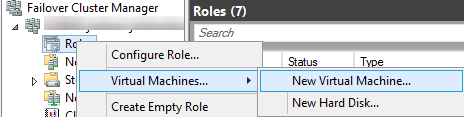
Open Failover Cluster Manager, then click on Roles, you should see list of VM’s, select the one you want to delete, then right on it and select Remove.
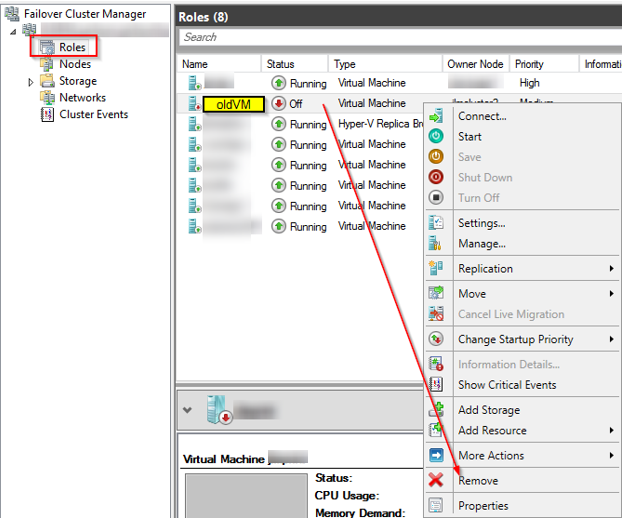
You will get

Then go to Hyper-V host where VM was running from, so you can remove from list
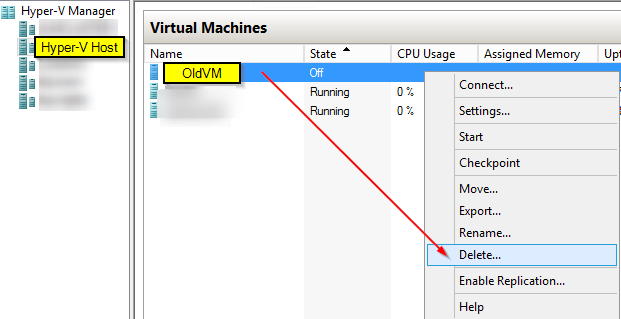
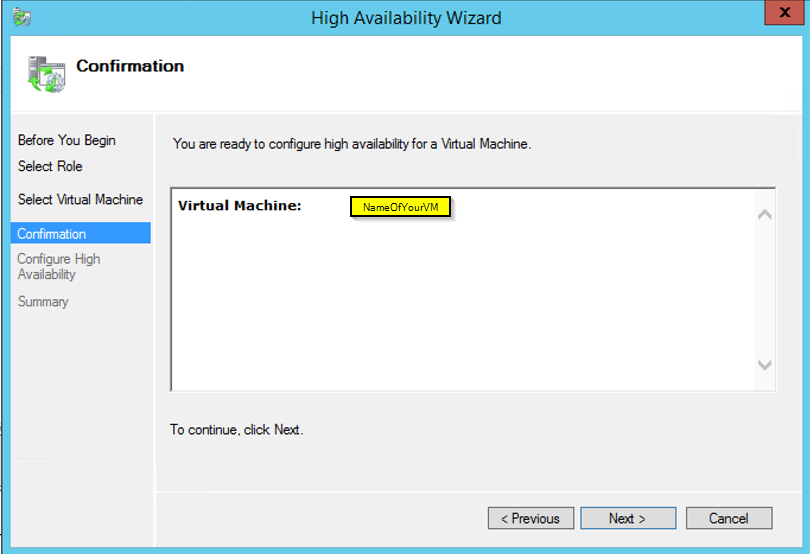
Confirmation are you sure you want to
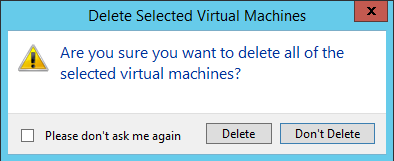
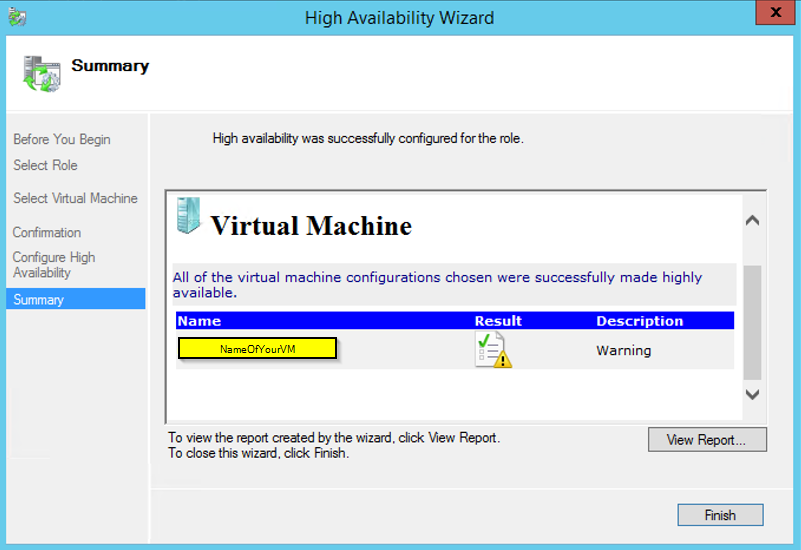
Now the VM is deleted from Cluster and remove from Hyper-V host, it’s time to delete the VM disk, by going to the location you looked at before you deleted the VM. That should give you back the storage space. That’s it, you get an error check the windows log or application log, it will give you more info.